- UNIT-I
 Introduction to E-Commerce
Introduction to E-Commerce The Scope of Electronic Commerce
The Scope of Electronic Commerce  Definition of Electronic Commerce,
Definition of Electronic Commerce, Electronic E-commerce and the Trade Cycle
Electronic E-commerce and the Trade Cycle Electronic Markets, Electronic Data Interchange
Electronic Markets, Electronic Data Interchange Internet Commerce, E-Commerce in Perspective
Internet Commerce, E-Commerce in Perspective Business Strategy in an Electronic Age: Supply Chains
Business Strategy in an Electronic Age: Supply Chains Porter’s Value Chain Model, Inter-Organizational Value Chains
Porter’s Value Chain Model, Inter-Organizational Value Chains Competitive Strategy, Porter’s Model
Competitive Strategy, Porter’s Model First Mover Advantage Sustainable Competitive Advantage
First Mover Advantage Sustainable Competitive Advantage Competitive Advantage using E-Commerce
Competitive Advantage using E-Commerce Business Strategy, Introduction to Business Strategy
Business Strategy, Introduction to Business Strategy Strategic Implications of IT, Technology
Strategic Implications of IT, Technology Business Environment, Business Capability
Business Environment, Business Capability Exiting Business Strategy, Strategy Formulation & Implementation Planning
Exiting Business Strategy, Strategy Formulation & Implementation Planning E-Commerce Implementation
E-Commerce Implementation E-Commerce Evaluation
E-Commerce Evaluation Business-to-Business Electronic Commerce
Business-to-Business Electronic Commerce Characteristics of B2B EC
Characteristics of B2B EC Models of B2B Ec
Models of B2B Ec Procurement Management Using the Buyer’s Internal Marketplace
Procurement Management Using the Buyer’s Internal Marketplace Just in Time Delivery
Just in Time Delivery B2B Models
B2B Models Auctions and Services from Traditional to Internet-Based EDI
Auctions and Services from Traditional to Internet-Based EDI The Role of Software Agents for B2B EC
The Role of Software Agents for B2B EC Electronic marketing in B2B
Electronic marketing in B2B Solutions of B2B EC
Solutions of B2B EC Managerial Issues
Managerial Issues Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) EDI: The Nuts and Bolts
EDI: The Nuts and Bolts EDI & Business
EDI & Business Internet and Extranet
Internet and Extranet The Largest Extranet,
The Largest Extranet,Architecture of the Internet
 Intranet and Extranet Intranet software ,Applications of Intranets
Intranet and Extranet Intranet software ,Applications of Intranets Intranet Application Case Studies
Intranet Application Case Studies Considerations in Intranet Deployment
Considerations in Intranet Deployment The Extranets, The structures of Extranets
The Extranets, The structures of ExtranetsExtranet products & services
 Applications of Extranets,Business Models of Extranet Applications, Managerial Issues
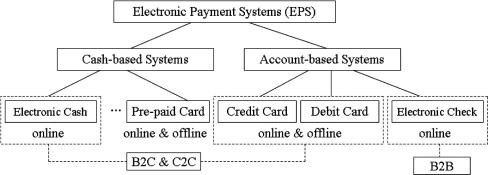
Applications of Extranets,Business Models of Extranet Applications, Managerial Issues Electronic Payment Systems,Is SET a failure
Electronic Payment Systems,Is SET a failureElectronic Payments & Protocols
 Security Schemes in Electronic payment systems, Electronic Credit card system on the Internet
Security Schemes in Electronic payment systems, Electronic Credit card system on the Internet Electronic Fund Transfer and Debit cards on the Internet
Electronic Fund Transfer and Debit cards on the Internet Stored – value Cards and E-Cash,Electronic Check Systems
Stored – value Cards and E-Cash,Electronic Check Systems Prospect of Electronic Payment Systems,
Prospect of Electronic Payment Systems,Managerial Issues
Automotive Network Exchange
Automotive Network Exchange
The Automotive Network Exchange is the private extranet initially set up and maintained by the Automotive Industry Action Group, Telcordia, General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler. It was built as a private network for the auto industry in 1995 to provide consistent, reliable speed and guaranteed security for data transmissions between the automakers and their suppliers. The ANX Network allows trading partners to collaborate electronically on product design and development; solicit and process orders; and facilitate just-in-time manufacturing and post shipping schedules.[3] In 1999 the Automotive
"an electronic payment system is a way of paying for a goods or services electronically, instead of using cash or a check, in person or by mail"
"an electronic payment system is a way of paying for a goods or services electronically, instead of using cash or a check, in person or by mail"
types of Electronic Payment Systems
- Automated clearing house (ACH)
- Wire transfers.
- Item processing (IP)
- Remote deposit capture (RDC)
- Fed Line Access Solutions.
- Automated Teller Machines.
- Card Services (ATM, credit, debit, prepaid)
- Mobile payments.
Designing Electronic Payment Systems
- Privacy. A user expects to trust in a secure system; just as the telephone is a safe and private medium free of wiretaps and hackers, electronic communication must merit equal trust.
- Security. A secure system verifies the identity of two-party transactions through “user authentication” and reserves flexibility to restrict information/services through access control. Tomorrow’s bank robbers will need no getaway cars just a computer terminal, the price of a telephone call, and a little ingenuity. Millions of dollars have been embezzled by computer fraud. No systems are yet fool-proof, although designers are concentrating closely on security.
- Intuitive interfaces. The payment interface must be as easy to use as a telephone. Generally speaking, users value convenience more than anything.
- Database integration. With home banking, for example, a customer wants to play with all his accounts. To date, separate accounts have been stored on separate databases. The challenge before banks is to tie these databases together and to allow customers access to any of them while keeping the data up-to-date and error free.
- Brokers. A “network banker”-someone to broker goods and services, settle conflicts, and facilitate financial transactions electronically-must be in place.
EPS -Is SET a failure Electronic Payments & Protocols
the Protocols that are used in E-Payments
Electronic installment frameworks are multiplying in banking, retail, human services, on-line showcases, and even government truth be told, anyplace cash needs to change hands. Associations are propelled by the need to convey items and administrations more expense viably and to give a higher caliber of administration to clients.
Examination into electronic installment frameworks for customers can be followed back to the 1940s, and the principal applications-Visas showed up before long. In the mid 1970s, the rising electronic installment innovation was marked electronic finances move (EFT).
Examination into electronic installment frameworks for customers can be followed back to the 1940s, and the principal applications-Visas showed up before long. In the mid 1970s, the rising electronic installment innovation was marked electronic finances move (EFT).
Work on EFT can be segmented into three broad categories:
Banking and financial payments
- Large-scale or wholesale payments (e.g., bank-to-bank transfer)
- Small-scale or retail payments (e.g., automated teller machines and cash dispensers)
- Home banking (e.g., bill payment)
On-line electronic commerce payments
- Token-based payment systems
Electronic cash (e.g., DigiCash)
Electronic checks (e.g., NetCheque)
Smart cards or debit cards (e.g., Mondex Electronic Currency Card)
- Credit card-based payment systems
Encrypted credit cards (e.g., World Wide Web form based encryption)
Third-party authorization numbers (e.g., First Virtual)
Secure Electronic Transaction (SET) Protocol
SET protocol was initially designed by Visa and MasterCard in 1997 and has evolved since then. SET protocol meets the four security requirements for EC as SSL(Secure Socket Layer) does: authentication, encryption, integrity, and non repudiation.
The role of payment gateway is to connect the Internet and proprietary networks of banks. Each participating entity needs its own certificate. To keep the consumer’s certificate in his or her personal computer or IC card, software called the electronic wallet, or digital wallet, is necessary. To connect the dig-ital wallet with various merchants, interoperability is a very important characteristic to meet.
Electronic Wallet
To achieve perfect security, the electronic wallet has to be downloaded into the buyer’s personal computer. Since the interoperability of the cardholder’s digital wallet with any merchant’s software is essential, a consortium of companies (Visa, MasterCard, JCB, and American Express) has established a company called SETCo (Secure Electronic Transaction LLC 1999).
Storage of Certificates
If the private key and corresponding public key in a certificate are physically stored in the customer’s personal computer, the customer can use the certificate only at the computer. However, if the certificate is stored in an IC card, the wallet can work if the IC card is inserted into a card reader attached to a computer.
The SET protocol, on the other hand, hides the customer’s credit card information from merchants and also hides the order information from banks to protect privacy. This scheme is called dual signature. Until SET becomes popular, a simple version of SSL is a very viable alternative.









No comments:
Post a Comment