- UNIT-I
 The Advantages of Interactive Graphics
The Advantages of Interactive Graphics Representative Uses of Computer Graphics
Representative Uses of Computer Graphics  Classification of Application Development of Hardware and software for computer Graphics
Classification of Application Development of Hardware and software for computer Graphics Overview, Scan:
Overview, Scan: Converting Lines
Converting Lines Scan Converting Circles
Scan Converting Circles Scan Converting Ellipses
Scan Converting Ellipses Hardcopy Technologies
Hardcopy Technologies Display Technologies
Display Technologies Raster-Scan Display System
Raster-Scan Display System Video Controller
Video Controller Random-Scan Display processor
Random-Scan Display processor Input Devices for Operator Interaction
Input Devices for Operator Interaction Image Scanners
Image Scanners Working exposure on graphics tools like Dream Weaver, 3D Effects etc
Working exposure on graphics tools like Dream Weaver, 3D Effects etc Clipping
Clipping Southland- Cohen Algorithm
Southland- Cohen Algorithm Cyrus-Beck Algorithm
Cyrus-Beck Algorithm Midpoint Subdivision Algorithm
Midpoint Subdivision Algorithm Geometrical Transformation
Geometrical Transformation 2D Transformation
2D Transformation Homogeneous Coordinates and Matrix Representation of 2DTransformations
Homogeneous Coordinates and Matrix Representation of 2DTransformations  composition of 2D Transformations
composition of 2D Transformations The Window-to-Viewport
The Window-to-ViewportTransformations
 Multimedia Definition
Multimedia Definition CD-ROM and the multimedia highway
CD-ROM and the multimedia highway Computer Animation
Computer Animation(Design, types of animation, using different functions)
 Uses of Multimedia
Uses of Multimedia Introduction to making multimedia –
Introduction to making multimedia – The stage of Project
The stage of Project hardware & software requirements to make good multimedia skills
hardware & software requirements to make good multimedia skills Training opportunities in Multimedia Motivation for Multimedia usage
Training opportunities in Multimedia Motivation for Multimedia usageSpatial Partitioning Representations
it is used to describe interior properties, by partitioning the spatial region, containing an object into a set of small, non-overlapping, contiguous solids. e.g. 3D object as Octree representation.
a solid is decomposed into a collection of adjoining, nonintersecting solids using spatial partitioning representations,. A quadtree is a representation format used to encode images. The fundamental idea behind the quadtree is that any image can be split into four quadrants. Each quadrant may again be split into four sub-quadrants, etc. In the quadtree, a parent node represents the image, while four child nodes, in a predetermined order, represent the four quadrants.
The following are different spatial partitioning techniques:
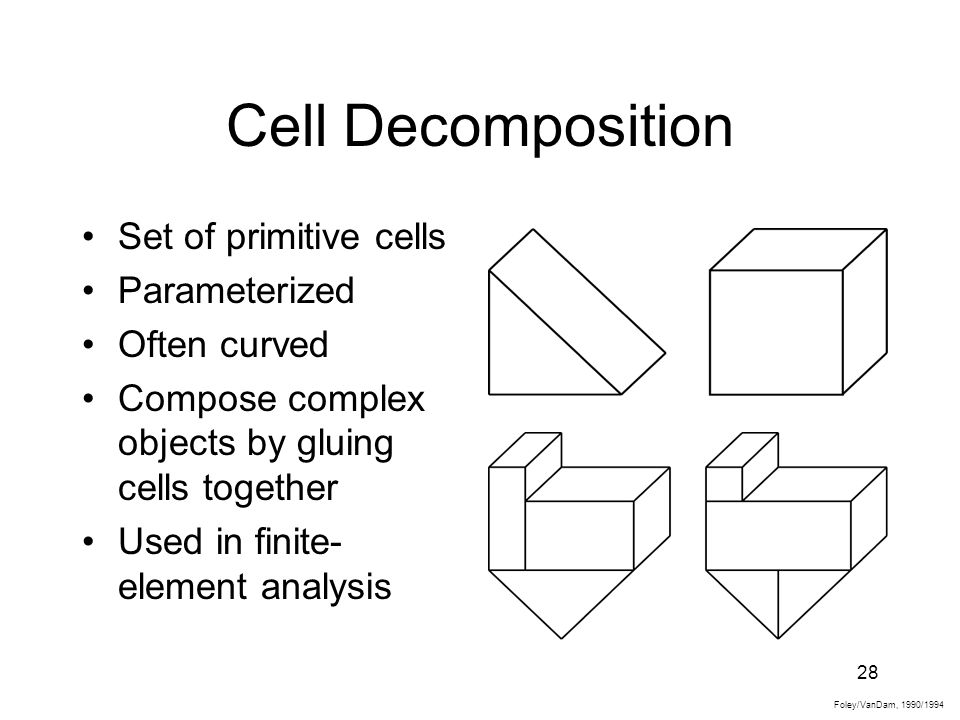
1.Cell Decomposition
2.Spatial Occupancy Enumeration
3.Quadtrees and Octrees










No comments:
Post a Comment