BCA
May 08, 2020
Computer graphics Sort Question Answer BCA Unit IV
1.
What are the various representation schemes used in three-dimensional objects?
Boundary representation (B-res) – describe the 3 dimensional
object as a set of surfaces that
separate the object interior from the environment.
Space-portioning representation – describe
interior properties, by partitioning the spatial region containing
an object into a set of small, no
overlapping, contiguous solids.
2.
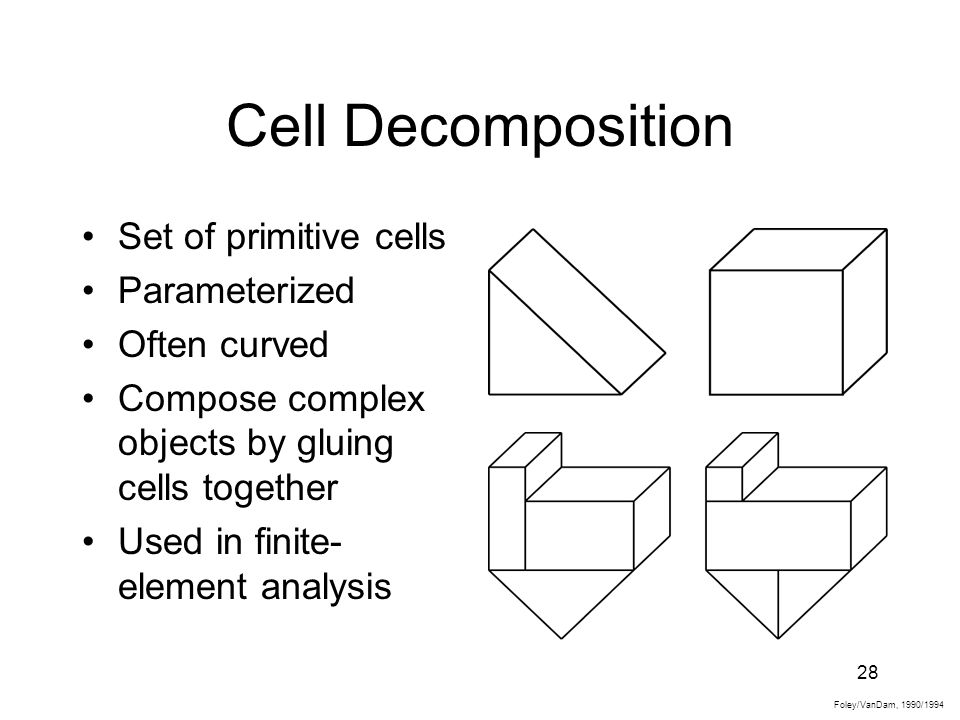
What is Polygon mesh?
A polygon mesh is a method to represent the polygon when the object
surfaces are tiled, it is more
convenient to specify the surface facets with a mesh function. The
various meshes are
Σ Triangle strip – (n-2) connected triangles
Σ Quadrilateral mesh – generates (n-1)(m-1)
Quadrilateral
3.
Define the B-Spline curve.
A B-Spline curve is a set of piecewise(usually cubic) polynomial
segments that pass close to a set of control points. However the curve does not pass through these
control points, it only passes close to them.
4.
What is a spline?
To produce a smooth curve through a designed set of points, a flexible strip called spline is used. Such a spline curve can be mathematically described with the piecewise cubic polynomial function whose first and second derivatives are continuous across various
curve section.
5.
What is the use of control points?
Spline curve can be specified by giving a set of coordinate
positions called control points, which indicates the general shape of the curve, can specify spline
curve.
6.
What are the different ways of specifying a spline curve?
Σ Using a set of boundary conditions that are
imposed on the spline.
Σ Using the state matrix that characteristics the
spline
Σ Using a set of blending functions that calculate
the positions along the curve path by
specifying a combination of geometric constraints on the curve.
7.
What are the important properties of Bezier Curve?.
It needs only four control points
• It always passes through the first and last control points
• The curve lies entirely within the convex half-formed by four
control points.
8.
Differentiate between interpolation spline and approximation spline.
When the spline curve passes through all the control points then
it is called interpolate. When the curve is not passing through all the control points then that
curve is called approximation spline.
9.
What is a Blobby object?
Some objects do not maintain a fixed shape but change their
surface characteristics in certain motions or when in proximity to other objects. That is known as
blobby objects. Example – molecular
structures, water droplets.
10. Define
Octrees.
Hierarchical
tree structures called octrees are used to represent solid objects in some
graphics systems.
Medical imaging and other applications that require displays of object cross
sections commonly
use octree representation.
11. Define
Projection.
The
process of displaying 3D into a 2D display unit is known as projection. The
projection
transforms
3D objects into a 2D projection plane. The process of converting the
description of objects
from world coordinates to viewing coordinates is known as projection.
12. What do you
mean by view plane?
A
view plane is nothing but the film plane in the camera which is positioned and
oriented for a particular
shot of the scene.
13. What is
view-plane normal vector?
This a normal vector is the direction perpendicular to the view plane.
14. What is the various
representation schemes used in three-dimensional objects?
Boundary representation
(B-res) – describe the 3 dimensional
objects as a set of surfaces that separate the object interior from the
environment.
Space- portioning
representation – describe the interior
properties, by partitioning the spatial region containing an object into a set
of small, no overlapping, contiguous solids.
15. What is Polygon mesh?
A polygon mesh is a method to
represent the polygon, when the object surfaces are tiled, it is more
convenient to specify the surface facets with a mesh function. The various
meshes are
Triangle strip – (n-2)
connected triangles
Quadrilateral mesh – generates
(n-1)(m-1) Quadrilateral
16. What is a surface patch?
A single surface element can be
defined as the surface traced out as two parameters (u, v) take all possible
values between 0 and 1 in a two-parameter representation. Such a single surface
element is known as a surface patch.
17. What are the advantages
of rendering polygons by scan line method?
i. The max and min values of
the scan were easily found.
ii. The intersection of scan
lines with edges is easily calculated by a simple incremental method.
iii. The depth of the polygon
at each pixel is easily calculated by an incremental method.
18. What are the advantages
of rendering by patch splitting?
i. It is fast- especially on
workstations with a hardware polygon-rendering pipeline.
ii. Its speed can be varied by
altering the depth of sub-division.
19. Define the B-Spline curve
A B-Spline curve is a set of
piecewise (usually cubic) polynomial segments that pass close to a set of
control points. However the curve does not pass through these control points,
it only passes close to them.
20. What is a spline?
To produce a
smooth curve through a designed set of points, a flexible strip called spline
is used. Such a spline curve can be mathematically described with a piecewise
cubic polynomial function whose first and second derivatives are continuous
across various curve section.
21. What is the use of
control points?
Spline curve can be specified
by giving a set of coordinate positions called control points, which indicates
the general shape of the curve can specify a spline curve.
22. What are the different
ways of specifying a spline curve?
• Using a set of boundary
conditions that are imposed on the spline.
• Using the state matrix that
characteristics of the spline
• Using a set of blending
functions that calculate the positions along the curve path by specifying
combination of geometric constraints on the curve.
23. What are the important
properties of Bezier Curve?
• It needs only four control
points
• It always passes through the
first and last control points
• The curve lies entirely
within the convex half-formed by four control points.
24. Differentiate between
interpolation spline and approximation spline.
When the spline curve passes
through all the control points then it is called interpolate. When the curve is
not passing through all the control points then that curve is called
approximation spline.
25. What do you mean by
parabolic splines?
For parabolic splines, a
parabola is fitted through the first three points p1,p2,p3 of the data array of
kot points. Then a second parabolic arc is found to fit the sequence of points
p2, p3, p4. This continues in this way until a parabolic arc is found to fit
through points pn-2, pn-1, and pn. The final plotted curve is a meshing together
of all these parabolic arcs.
26. What is the cubic spline?
Cubic splines are a straight
forward extension of the concepts underlying parabolic spline. The total curve, in this case, is a sequence of arcs of cubic rather than parabolic curves
27. Define Octrees
Hierarchical tree structures
called octrees are used to represent solid objects in some graphics systems.
Medical imaging and other applications that require displays of object cross-sections commonly use octree representation.
28. Define Projection
The process of displaying 3D
into a 2D display unit is known as projection. The projection transforms 3D
objects into a 2D projection plane.
29. What are the steps
involved in 3D transformation?
- Modeling Transformation
-Viewing Transformation
-Projection Transformation
-Workstation
Transformation
30. What do you mean by the view
plane?
A view plane is nothing but the
film plane in the camera which is positioned and oriented for a particular shot of
the scene.
31. What is view-plane
normal vector?
This normal vector is the
direction perpendicular to the view plane and it is called as [DXN DYN DZN]
32. What is view distance?
The view a plane normal vector is a directed line segment from the view plane to the view
reference point. The length of this directed line segment is referred to as
view distance